There’s currently a lot of excitement surrounding Suffolk’s plans to use LoRaWAN and The Things Gateways to improve communication, processes and efficiency in the local region. Find out the key information with this handy blog as we cover IoT, LoRaWAN and what the future of these technologies has in store for our region.
What is the Internet of Things?
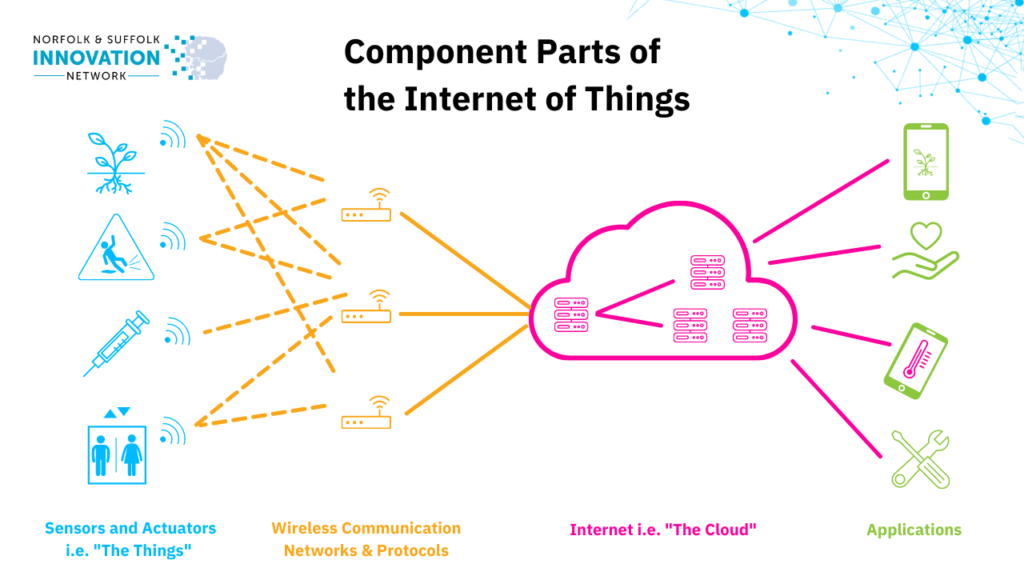
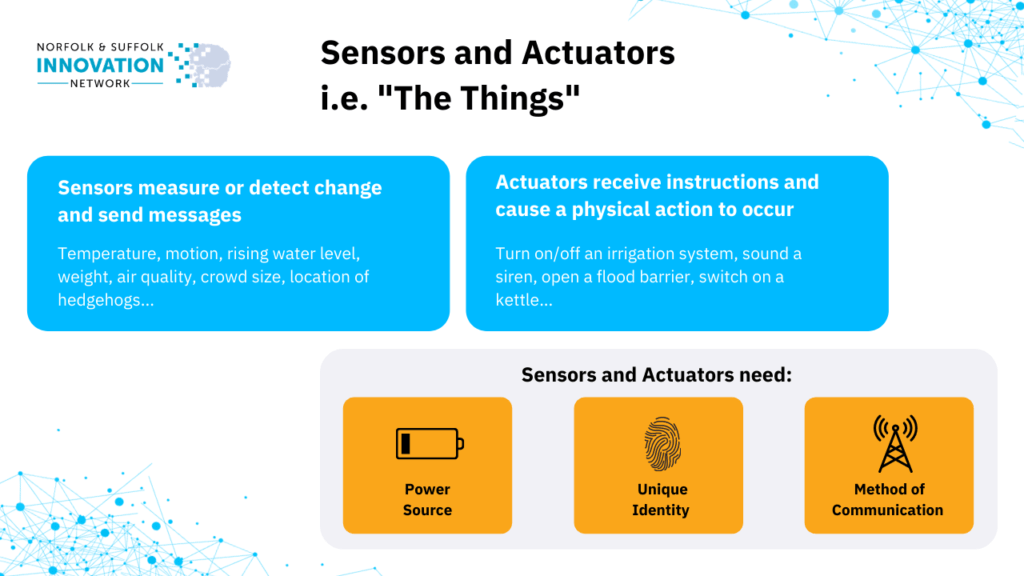
Put simply, IoT is a network of connected devices that communicate with each other to measure, record and display information as well as triggering actions in some cases.
If you think about the internet that we all know and use daily to communicate with each other as the ‘internet of people’, the Internet of Things largely the same except instead of humans there are things.
The beginnings of IoT devices can be traced back to the 80s, some students at Carnegie Mellon University didn’t want to keep making the trip down to the Coke vending machine just for it to be empty.
To solve this problem, they hacked the vending machine so that they would be able to check from their desks whether the vending machine was fully stocked but also the temperature of the machine so that they didn’t waste time going to get a warm can of Coke.
How does IoT benefit our lives and business operations?
IoT has the potential to improve many aspects of our consumers lives as well as streamlining and increasing efficiency for a variety of business processes.
Improved Decision Making
- Real-time data for effective predictive analytics
- We can collect data that would previously not been available
Improved Service Quality
- Potential faults can be identified and repaired before they occur
- 24/7 asset monitoring can be offered
Improved Profitability
- Reduced operational costs
- Enables new business models to emerge
What are some industries using IoT for?
IoT has use cases in every industry from health and social care to agriculture. Here are some examples of how it is being used by businesses in different sectors.
Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
IoT devices can be implemented into temperature-controlled storage facilities for products like the new Covid-19 vaccine which must be kept at a very low temperature. The devices can give early warning to senior managers and operations teams of any temperature control technology breakdowns so that repairs can be made before it is too late and the stock has to be wasted.
Agriculture
For crops grown indoors hydroponically, IoT devices can monitor and acutely adjust environmental conditions so that the best possible crops can be grown.
Health and Social Care
Wearable sensors can be given to the elderly or at-risk adults that alert a caregiver or family member if they have just had a fall. This can help injured or disoriented people get the help they need much more quickly.
Property Management
Automatic compliance checks can be carried out without the requirement for a maintenance worker to visit the property and carry out the checks by hand. For example, carbon monoxide detectors and emergency lighting real-time properties can be tested by built-in IoT monitoring devices.
What is LoRaWAN and The Things Network?
LoRaWAN is a wireless communication network that IoT devices can use to transmit messages between devices.
Its development is very important for business development as LoRaWAN creates opportunities to collect real-time data that helps businesses grow. Getting real time data today could be the next step towards the next big business idea of the future.
The Things Network was started in Amsterdam in 2015 and it has now evolved into a global network, with 17,000 gateways in 150 countries, with 135,000 contributors worldwide.
The Things Network gives private companies or members of the public the tools they need to set up Gateways which act as a bridge between devices and the Things Network – forwarding messages from IoT devices to the Internet.
What are the positives and negatives of LoRaWAN?
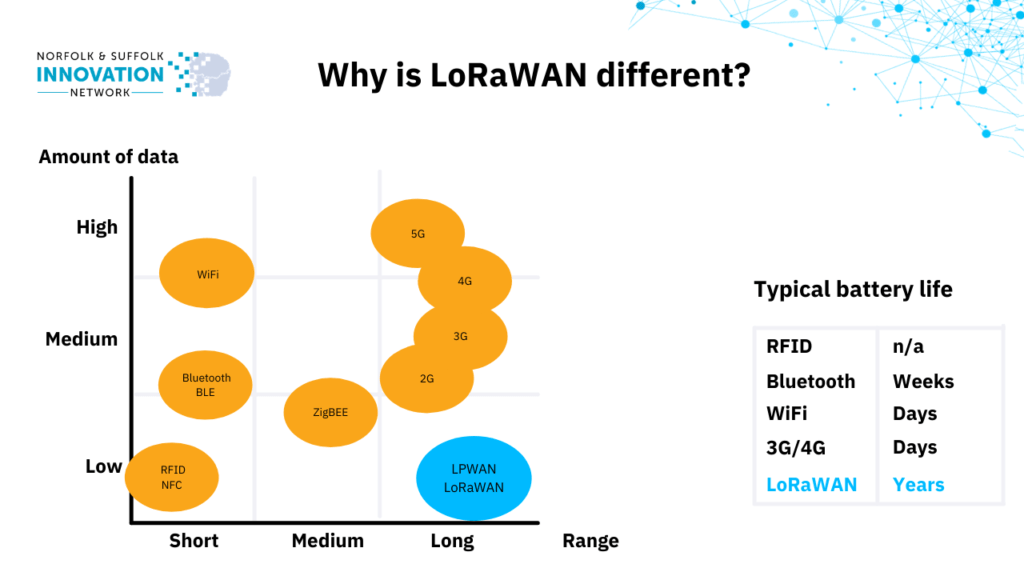
LoRaWAN can easily transmit small amounts of data over a long-range. Although the amount of data you can transmit is tiny (think less than a tweet), it’s perfect for sending small bits of data in a little and often approach, such as whether a security door has been left open or not, but this makes it unsuitable for a user to browse the internet for example.
LoRaWAN devices have much longer battery lives than Bluetooth devices for example – with LoRaWAN device batteries lasting years, compared to Bluetooth device batteries which only last a matter of weeks. This means that once the device is installed it doesn’t require much regular maintenance or upkeep.
Continuous streams of data cannot be transmitted so something like the temperature in a fridge cannot be constantly monitored but it can be communicated to the end-user as often as every five seconds or so. This means it’s not suitable for situations where constant monitoring is required or in truly mission-critical scenarios.
Because LoRaWAN devices are battery-operated, they can be retrofitted quite easily and do not incur extra implementation costs for rewiring.
What does this technology mean for the development of Suffolk?
Over 30 local authorities within the U.K are looking to use LoRaWAN to improve their services and operations but Suffolk and Norfolk are much further ahead than most.
Currently, there are plans for 220 Gateways to go up in the Norfolk and Suffolk region.
Projects funded by the U.K government have allowed for new innovative research and technological developments to take place in Suffolk. Suffolk is unique in that we have urban, rural and coastal areas within the region so we have lots of opportunities to experiment with different environments.
One example of this is the implementation of sensors that monitor road surface temperatures to revolutionise the way gritting is done – leading to monetary savings and reduced climate impact.
Another example is the use of air quality monitors in street lights to give a better understanding of the harmful gases we are ingesting daily.
Alternatively, sensors can monitor silt and water levels in gulleys to alert the relevant areas to any intervention that is required, instead of remaining reliant on cyclical management which isn’t always 100% accurate.
To allow vulnerable adults to be able to stay in their own homes for longer and allow them to be independent for as long as they want to be, sensors and wearables can be used to monitor patterns to detect possible issues.
For example, if an older adult always puts the kettle on at around the same time every morning but suddenly, one day doesn’t, authorities or caregivers can be alerted.
As well as this, location tracking can be used in conjunction with wearables – if this person usually travels out of the house to the post office and no further but one day they do, a responsible person can be alerted.
LoRaWAN Uses for Different Types of Areas
LoRaWAN and IoT devices will be used by local government authorities in different ways depending on the area they will be placed in.
In urban areas, some good examples of use cases include:
- Parking space sensors
- Population flow management
- Infrastructure monitoring
- Flood prevention and warnings
In rural areas, some examples of good use cases include:
- Remote site/equipment monitoring
- On-demand maintenance
- Precision farming
- Property security
In-home or office environments, some good use cases include:
- Energy management
- Occupancy or activity monitoring
- Leak detection
- Greenhouse/allotment monitoring
In industrial settings, some good use cases include:
- Predictive maintenance
- Supply chain management
- Goods condition monitoring
- Pollution monitoring
Do you have an idea for an IoT project?
At Coderus, we specialise in creating bespoke IoT solutions, working with clients from a variety of industries to create the perfect solution for their business needs.
Get in touch with us today so we can help you bring your project to life.























